Artificial rain, also known as cloud seeding or weather modification, introduces substances into clouds to enhance precipitation. Here’s an overview:
Methods:
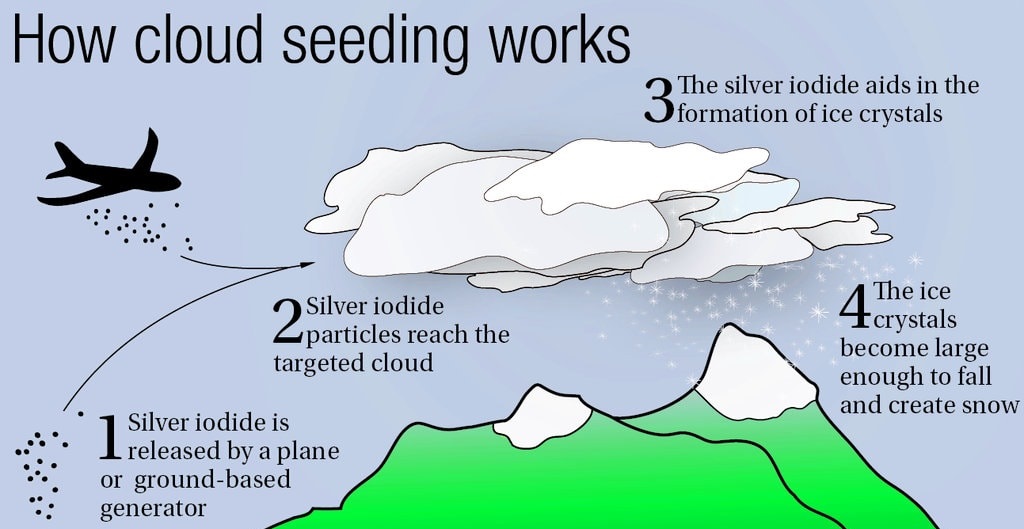
- Cloud Seeding: Silver iodide or dry ice is injected into clouds to stimulate ice crystal formation and enhance precipitation.
- Rain Enhancement: Salt or other substances are introduced into clouds to increase rainfall.
- Weather Modification: Various techniques, including cloud seeding, are used to alter weather patterns.
Techniques:
- Aircraft Seeding: Planes disperse substances into clouds.
- Ground-Based Generators: Machines release substances into the air.
- Rockets: Pyrotechnic rockets inject substances into clouds.
- Cloud Seeding Towers: Ground-based structures release substances.
Substances Used:
- Silver Iodide: Enhances ice crystal formation.
- Dry Ice: Stimulates cloud convection.
- Salt: Increases rainfall.
- Other substances: Calcium chloride, urea, and more.
Process:
- Nucleation: Substances interact with cloud droplets.
- Cloud Selection: Identify suitable clouds for seeding.
- Substance Dispersion: Release substances into clouds.
- Precipitation Enhancement: Stimulated clouds produce precipitation.
Benefits:
- Drought Relief
- Water Resource Management
- Flood Control
- Agricultural Benefits
- Weather Pattern Modification
Challenges and Limitations:
- Efficacy Debate
- Unintended Consequences
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Environmental Concerns
- Regulatory Frameworks
Real-World Examples:
- China’s Weather Modification Program
- India’s Cloud Seeding Program
- United States Weather Modification Research
- Russia’s Cloud Seeding Efforts
Future Developments:
- Advanced Weather Modeling
- Nanotechnology Applications
- Bio-inspired Cloud Seeding
- International Cooperation and Regulation
Keep in mind that artificial rain is still a developing science, and its effectiveness and implications are debated among experts.





